Tel:+8618337312531
Email: sale@graphitesmold.com
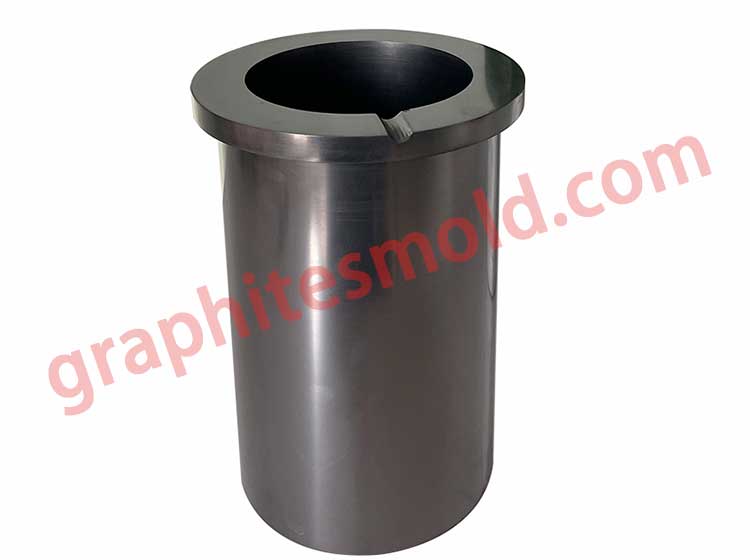
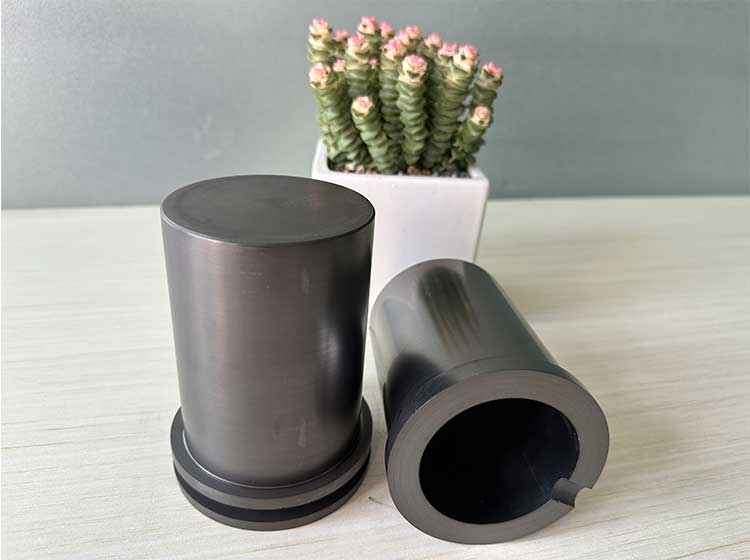
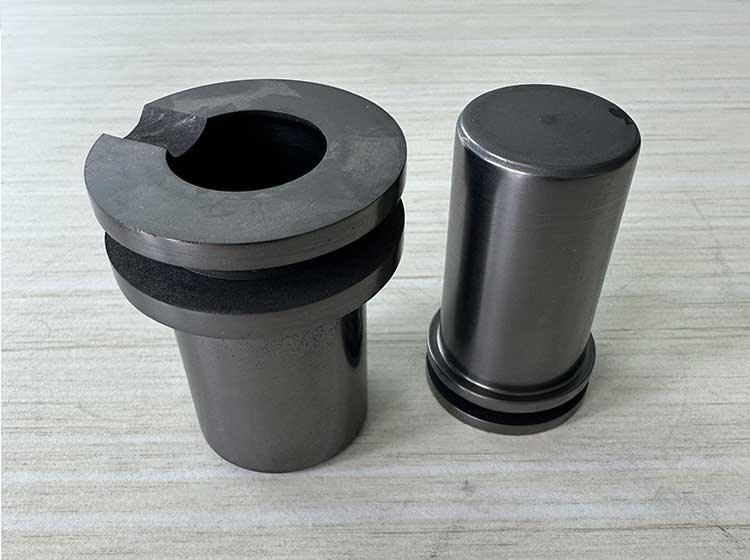
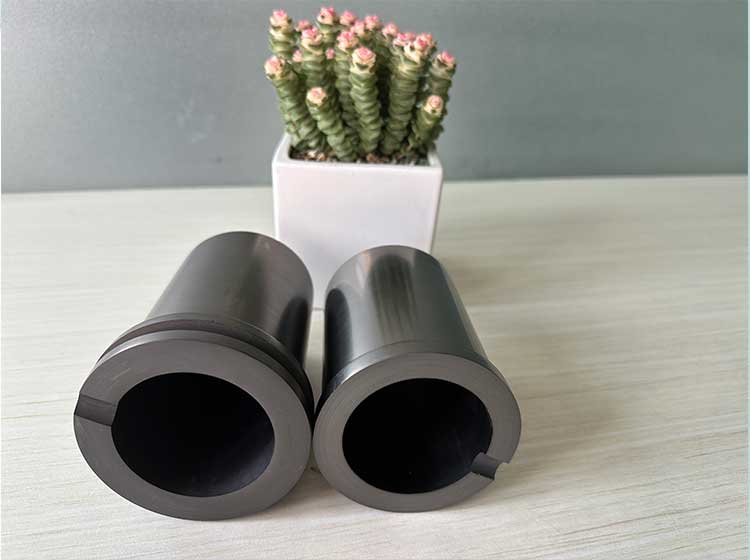
Graphite crucible, also known as molten copper ladle, molten copper, etc., refers to a type of crucible made of graphite, clay, silica and wax stone as raw materials.
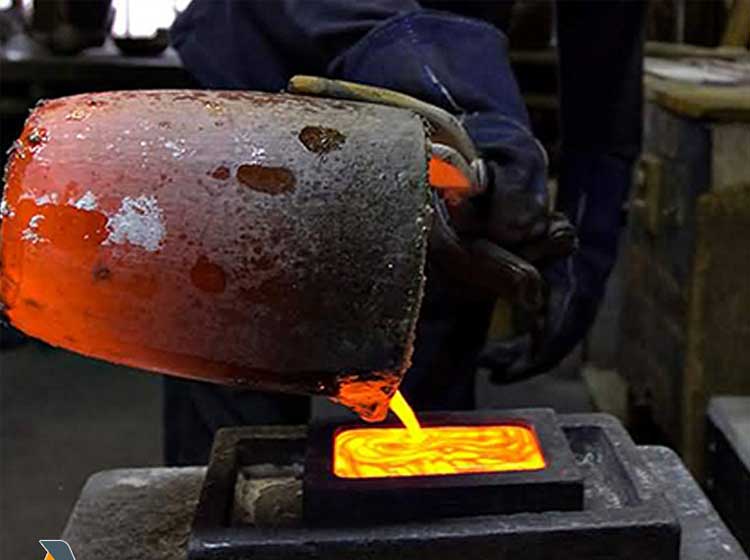
Graphite crucible is mainly used to smelt non-ferrous metals and their alloys such as copper, brass, gold, silver, zinc and lead.
The crucible is a refractory graphite crucible made of crystallized natural graphite as the main raw material and plastic refractory clay as the binder. The graphite crucible is an important part of the performance and application of refractory materials. It has a small thermal expansion coefficient during high-temperature use and has certain strain resistance to rapid cooling and rapid heating.
It has strong corrosion resistance to acidic and alkaline solutions, has excellent chemical stability, and does not participate in any chemical reactions during the smelting process.
The inner wall of the graphite crucible is smooth, and the molten metal liquid is not easy to leak and adhere to the inner wall of the crucible, making the metal liquid have good fluidity and casting properties, and is suitable for casting in various molds.
It is precisely because of the above characteristics that graphite crucibles are mainly used for melting special alloy steel, non-ferrous metals and their alloys, and are used in combination with different types of clinker.